FAQ
This list is regularly updated with recent and common questions Kameleoon regularly receives from customers.
What are the Kameleoon domains that I need to whitelist?
If your website restricts the loading of resources (scripts, images, media, CSS) via the standard Content-Security-Policy (CSP) HTTP header, you'll need to update your site's CSP to allow Kameleoon resources to load.
Easy setup (with wildcards)
script-src always trumps default-src, don't use this setup if you already use the complete setup in your CSP.
Below is the additional content for the CSP header. Add it to your own configuration.
default-src https://*.kameleoon.com https://*.kameleoon.io https://*.kameleoon.eu https://*.kameleoon.net https://*.experimentation.dev;
Complete setup (fully detailed)
Kameleoon regularly adds new features to the product, which could result in additional URLs. Be careful to list all of the possible hosts and resource types (script, image, etc) explicitly; add this additional content to the CSP header.
Replace [your-site-code] with your Kameleoon site code in each line that it appears and add this to your configuration:
script-src https://[your-site-code].kameleoon.xx https://static.kameleoon.com https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com https://simulation.kameleoon.com https://client-config.kameleoon.com https://sdk-config.kameleoon.eu https://electra.kameleoon.com https://aibuilder.kameleoon.com https://static.experimentation.dev 'unsafe-eval';
style-src https://static.kameleoon.com https://static.products.kameleoon.com https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com https://simulation.kameleoon.com https://electra.kameleoon.com https://aibuilder.kameleoon.com https://static.experimentation.dev 'unsafe-inline';
connect-src https://[your-site-code].kameleoon.xx https://static.kameleoon.com https://eu-data.kameleoon.io https://eu-data.kameleoon.eu https://na-data.kameleoon.io https://na-data.kameleoon.eu https://editor.kameleoon.com https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com https://simulation.kameleoon.com https://api.kameleoon.com https://customers.kameleoon.com https://logger.kameleoon.io https://client-config.kameleoon.com https://sdk-config.kameleoon.eu https://api.products.kameleoon.com https://static.experimentation.dev https://sdk-config.experimentation.dev https://eu-data.experimentation.dev;
img-src https://[your-site-code].kameleoon.xx https://storage.kameleoon.eu https://storage.kameleoon.io https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com https://simulation.kameleoon.com https://static.kameleoon.com https://images.products.kameleoon.com https://static.experimentation.dev;
frame-src 'self' https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com https://static.experimentation.dev;
Each of the URLs in the CSP policy serves a specific purpose:
Web Experimentation
https://[your-site-code].kameleoon.xx– Used to load the Kameleoon Web Experimentation Application Script,engine.js(previously namedkameleoon.js).https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)– Used for tracking purposes.https://logger.kameleoon.io– Used to send tracking data for logging purposes.https://data.kameleoon.net– Required if you use Kameleoon Simulation tool to QA experiments across multiple subdomains.
Feature Experimentation (Client-side SDKs)
https://client-config.kameleoon.com– Required for SDK versions < 2.1.0.https://sdk-config.kameleoon.eu– Required for SDK versions >= 2.1.0.https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)– Used for tracking purposes.https://logger.kameleoon.io– Used to send tracking data for logging purposes.
Graphic Editors
https://static.kameleoon.com– (deprecated) Used to load static resources for the old graphic editor.https://editor.kameleoon.com– (deprecated) Used by the old graphic editor.https://graphical-editor.kameleoon.com– Used by the new graphic editor.https://storage.kameleoon.(eu|io)– Used to load images used in experiments created with the graphic editors.
Prompt-Based Experimentation (PBX)
https://aibuilder.kameleoon.com– Used by the prompt-based editor.https://electra.kameleoon.com– Used by the prompt-based editor.https://storage.kameleoon.(eu|io)– Used to load images in the prompt-based editor.https://api.kameleoon.com– Used to load account-related information.https://sdk-config.kameleoon.eu– Used to control Kameleoon feature flags activated in the prompt-based editor.
Simulation
https://api.kameleoon.com– Used by the old simulation.https://simulation.kameleoon.com– Used by the new simulation.
Product Recommendation
https://static.products.kameleoon.com– Used to load resources for the Product Recommendation module.https://api.products.kameleoon.com– API used by the Product Recommendation module.https://images.products.kameleoon.com– Used to load product images for recommendations.
APIs & Integrations
https://api.kameleoon.com– Required if you intend to use the Automation API for testing directly from the browser.https://customers.kameleoon.com– Required if you use the SDK API or a custom integration developed by Kameleoon.
Internal Ressources
By default, engine.js does not include simulation paths or application-specific information to minimize script size. To provide these details, the full script kameleoonFull.js must be loaded, which supplies engine.js with all necessary data on internal resources and loading instructions.
https://static.kameleoon.com– Used to load internal resources.https://static.experimentation.dev– Used to load internal resources.https://sdk-config.experimentation.dev– Used to control Kameleoon feature flags activated in the Kameleoon product.https://eu-data.experimentation.dev– Used to send tracking data for logging purposes.
The domain for your Kameleoon scripts https://[your-site-code].kameleoon.xx may vary from one project to another. Your projects may be hosted on either kameleoon.eu or kameleoon.io depending on their creation date. Make sure you use the domain displayed in your project in the Kameleoon App.
Will Kameleoon’s script (engine.js) slow down my website?
No. Kameleoon’s script is built with cutting-edge technology to run asynchronously (when using the async installation snippet) and is fully cached by the browser for 90 minutes, so it never blocks page loading, even during rare CDN incidents (99.99% uptime). On average, the script loads in under 70ms over a 4G connection or faster network conditions.
Kameleoon further minimizes impact through advanced compression techniques, combining TypeScript and Brotli, resulting in a base script size of just 28.4 KB.
Important considerations
Script size may increase depending on the number of experiments you run and their content (CSS/JavaScript).
For experiments or personalization campaigns that do not need to load immediately, the “DELAYED” tag is recommended. This delays loading non-essential experiments until after the first page load. Kameleoon intelligently manages these: configuration is only downloaded after 10 seconds of idle time or when a visitor is targeted and allocated a variation other than the control. This approach ensures minimal impact on load performance while still delivering full functionality for prioritized experiments.
Why does the Kameleoon engine (engine.js application file) use the eval() function?
The Kameleoon JavaScript engine requires the eval() function to add custom code to Kameleoon, such as custom data and custom JavaScript, when implementing variations of a page. Using the eval() function allows Kameleoon to dynamically execute this custom code at runtime.
If you use a Content Security Policy (CSP) directive that prevents the eval() function's use, you can implement the following JavaScript snippet before the Kameleoon installation tag:
<script>
window.kameleoonQueue = window.kameleoonQueue || [];
function excludeKameleoonEval() {
Kameleoon.Utils.runProtectedScript = function (code, fileName) {
const script = document.createElement("script");
const wrappedCode = "(function () {\n" + code + "\n})();";
script.innerHTML = wrappedCode;
if (fileName) {
script.innerHTML += "\n//# sourceURL=" + fileName;
}
document.head.appendChild(script);
};
}
kameleoonQueue.push({
level: "IMMEDIATE",
command: excludeKameleoonEval
});
</script>
//Add the Kameleoon Installation tag here. Refer to this documentation: https://developers.kameleoon.com/web-experimentation/simple-implementation
<script src="//SITE_CODE.kameleoon.eu/engine.js" fetchpriority="high" async></script>
If your CSP blocks eval(), implementing the code snippet will not remove these restrictions. For full functionality, the relevant CSP directive must be adjusted to allow eval() or similar functions; otherwise, certain advanced targeting or customization features in Kameleoon remain inaccessible due to browser security enforcement.
The Kameleoon Graphic Editor (including the simulation panel) also requires the eval() function. However, you can work around this requirement by installing the Kameleoon Chrome Extension and enabling the Dev Tools > Tag injection > Bypass policies setting to override the policies locally. You must also provide your sitecode. Enabling the Bypass policies setting allows you to use the Graphic editor using a Chrome browser.
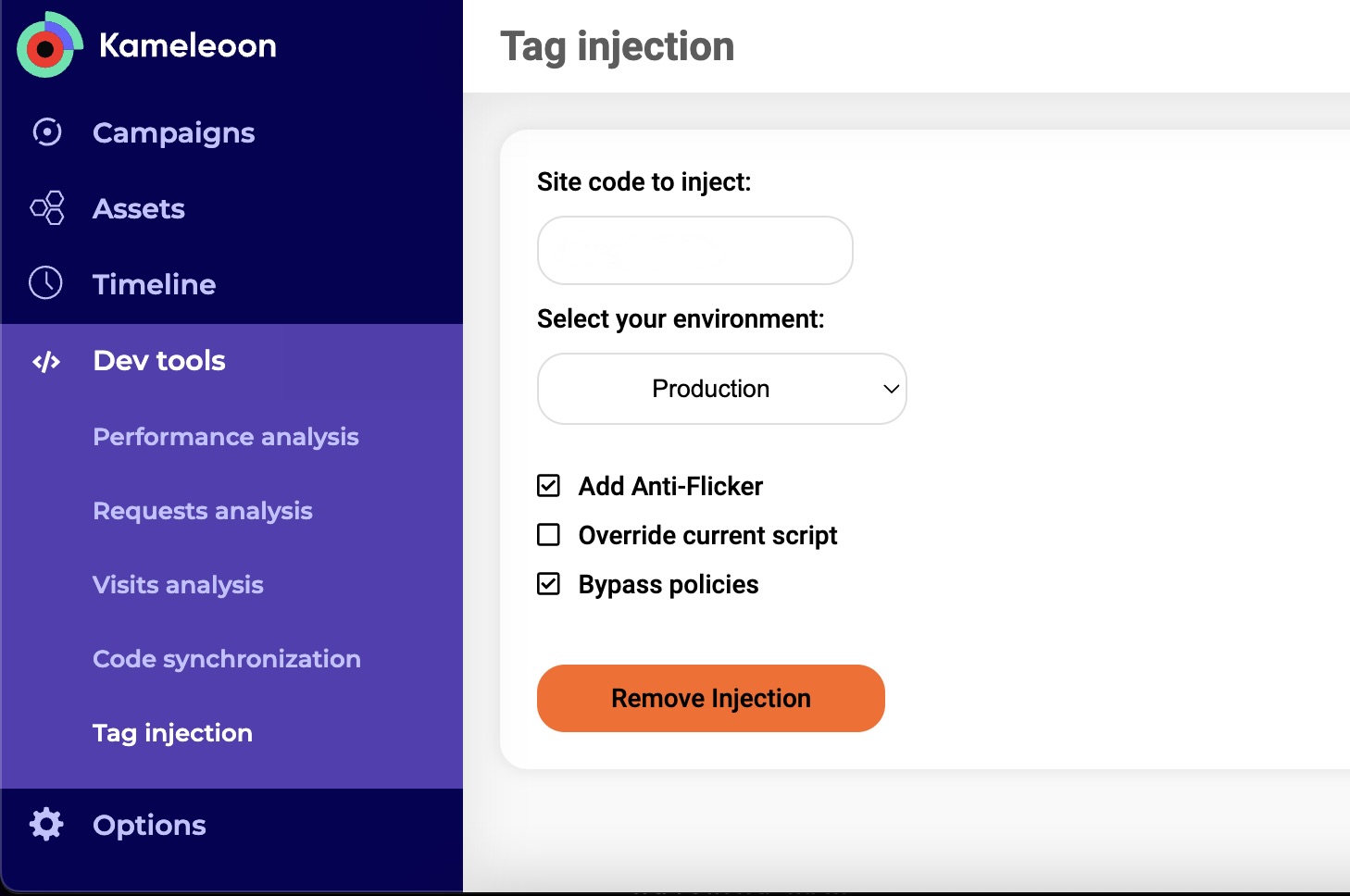
Some features of Kameleoon are not available if the eval() function is blocked with a CSP directive. These limitations apply even if you use any code snippet or workaround mentioned in the FAQ. The following features will remain unavailable unless your CSP explicitly allows eval():
- Targeting a segment with a custom JavaScript condition is now supported, but only when the condition runs asynchronously.
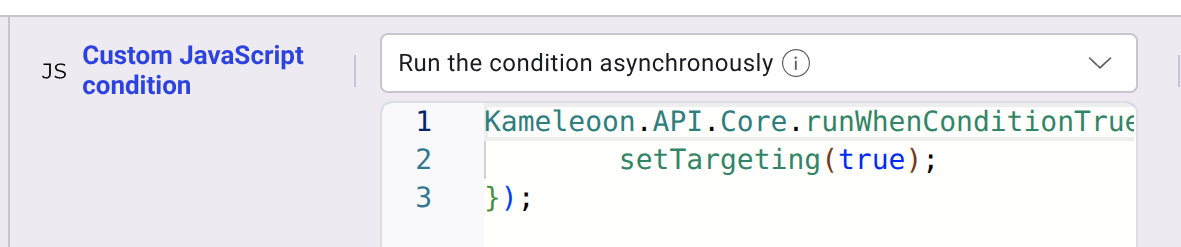
- Using custom data with custom JavaScript code.
- Using acquisition channels with custom JavaScript code.
Can I use my server to act as a proxy for Kameleoon's tracking calls?
Yes, Kameleoon offers this advanced option. Here's how it works: on your server, you must forward all HTTP requests received to (eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io). For example, if you chose tracking.yourdomain.com as your tracking domain, a tracking request would be a POST to "tracking.yourdomain.com". Your server listening on this domain should then forward the request, along with all the necessary data and parameters, to the (eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io) host. To enable this option, contact your Customer Success Manager.
When forwarding requests to (eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io), ensure the request URL is also rewritten to (eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io). It's not enough to forward the request to the server while keeping the original Host: HTTP header set to the domain (tracking.yourdomain.com). The Host: header must be set to (eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io).
Can I use Subresource Integrity (SRI) with the Kameleoon application file (script or iframe)?
Unfortunately, no. While SRI is a useful security feature in modern browsers, the application file changes over time. If it did not, many Kameleoon features would be unavailable. For example, starting and stopping experiments instantly without requiring a redeployment would be impossible. Since the contents of the file changes, the hash of the resource also changes, meaning SRI cannot be used. Otherwise, the resource would be blocked as soon as it updates on the servers.
With Kameleoon, on Firefox only, my website now loads with a huge flash/flicker effect. Why?
It's an known bug on Firefox. Until it's fixed properly by the Firefox team, there is a workaround: your linked CSS ressource should be followed by a <script> tag (even an almost empty one). Example:
<link href="https://www.example.com/web/style.css" media="all" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<script>/**/</script>
This will remove the flashing effect entirely.
Can I use minified versions of the installation tags?
Kameleoon scripts are already short, and using a minified version does not meaningfully affect page load time (the code is already compressed using Brotli or Gzip). Thus, minified versions are not recommended. However, if required, they are available below.
Asynchronous loading with anti-flicker
<script>
var a=1000;window.kameleoonQueue=window.kameleoonQueue||[];window.kameleoonStartLoadTime=new Date().getTime();if(!document.getElementById("kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet")&&!window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut){var b=document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0];var c="* { visibility: hidden !important; background-image: none !important; }";var d=document.createElement("style");d.type="text/css";d.id="kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet";if(d.styleSheet){d.styleSheet.cssText=c}else{d.appendChild(document.createTextNode(c))}b.parentNode.insertBefore(d,b);window.kameleoonDisplayPage=function(e){if(!e){window.kameleoonTimeout=true}if(d.parentNode){d.parentNode.removeChild(d)}};window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut=window.setTimeout(window.kameleoonDisplayPage,a)};
</script>
<script src="//SITE_CODE.kameleoon.eu/engine.js" fetchpriority="high" async></script>
Unify session data across subdomains
If you use the unified session data tag to unify session data across subdomains with either the synchronous tag or the asynchronous tag without antiflicker:
<script>
window.kameleoonIframeURL="https://www.customerdomain.com/path/to/kameleoon-iframe.html";var f=document.createElement("a");window.kameleoonLightIframe=false;f.href=window.kameleoonIframeURL;window.kameleoonIframeOrigin=f.origin||(f.protocol+"//"+f.hostname);if(location.href.indexOf(window.kameleoonIframeOrigin)!=0){window.kameleoonLightIframe=true;var g=function(event){if(window.kameleoonIframeOrigin==event.origin&&event.data.slice&&event.data.slice(0,9)=="Kameleoon"){window.removeEventListener("message",g);window.kameleoonExternalIFrameLoaded=true;if(window.Kameleoon){Kameleoon.Utils.runProtectedScript(event.data);Kameleoon.Analyst.load()}else{window.kameleoonExternalIFrameLoadedData=event.data}}};if(window.addEventListener){window.addEventListener("message",g,false)}var h=document.createElement("iframe");h.src=kameleoonIframeURL;h.id="kameleoonExternalIframe";h.style="float: left !important; opacity: 0.0 !important; width: 0px !important; height: 0px !important;";document.head.appendChild(h)};
</script>
If you use the unified session data tag to unify session data across subdomains and the asynchronous tag with anti-flicker, you must add the three script tags in the following order:
- Asynchronous tag with anti-flicker.
- Unified session data tag.
- Kameleoon installation tag.
<script>
var a=1000;window.kameleoonQueue=window.kameleoonQueue||[];window.kameleoonStartLoadTime=new Date().getTime();if(!document.getElementById("kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet")&&!window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut){var b=document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0];var c="* { visibility: hidden !important; background-image: none !important; }";var d=document.createElement("style");d.type="text/css";d.id="kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet";if(d.styleSheet){d.styleSheet.cssText=c}else{d.appendChild(document.createTextNode(c))}b.parentNode.insertBefore(d,b);window.kameleoonDisplayPage=function(e){if(!e){window.kameleoonTimeout=true}if(d.parentNode){d.parentNode.removeChild(d)}};window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut=window.setTimeout(window.kameleoonDisplayPage,a)};
</script>
<script>
window.kameleoonIframeURL="https://www.customerdomain.com/path/to/kameleoon-iframe.html";var f=document.createElement("a");window.kameleoonLightIframe=false;f.href=window.kameleoonIframeURL;window.kameleoonIframeOrigin=f.origin||(f.protocol+"//"+f.hostname);if(location.href.indexOf(window.kameleoonIframeOrigin)!=0){window.kameleoonLightIframe=true;var g=function(event){if(window.kameleoonIframeOrigin==event.origin&&event.data.slice&&event.data.slice(0,9)=="Kameleoon"){window.removeEventListener("message",g);window.kameleoonExternalIFrameLoaded=true;if(window.Kameleoon){Kameleoon.Utils.runProtectedScript(event.data);Kameleoon.Analyst.load()}else{window.kameleoonExternalIFrameLoadedData=event.data}}};if(window.addEventListener){window.addEventListener("message",g,false)}var h=document.createElement("iframe");h.src=kameleoonIframeURL;h.id="kameleoonExternalIframe";h.style="float: left !important; opacity: 0.0 !important; width: 0px !important; height: 0px !important;";document.head.appendChild(h)};
</script>
<script src="//SITE_CODE.kameleoon.eu/engine.js" fetchpriority="high" async></script>
Can I modify the installation tag Kameleoon provides?
Installation tags should not be modified. Their code has been extensively tested and optimized. Modifying them can result in a non-working setup. If an installation tag requires modification for any reason, please contact the Kameleoon Account Manager to coordinate with developers. Attempting this independently is strongly discouraged.
Can I add the installation tag in a separate external script?
You should not include any installation tag in its own separate, external script. For example, never do this:
<script src="resources/scripts/kameloon-loader.js" fetchpriority="high" async></script>
while the kameloon-loader.js script contains for instance the following installation code:
// Duration in milliseconds to wait while the Kameleoon application file is loaded
var kameleoonLoadingTimeout = 1000;
window.kameleoonQueue = window.kameleoonQueue || [];
window.kameleoonStartLoadTime = new Date().getTime();
if (!document.getElementById("kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet") && !window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut) {
var kameleoonS = document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0];
var kameleoonCc = "\* { visibility: hidden !important; background-image: none !important; }";
var kameleoonStn = document.createElement("style");
kameleoonStn.type = "text/css";
kameleoonStn.id = "kameleoonLoadingStyleSheet";
if (kameleoonStn.styleSheet) {
kameleoonStn.styleSheet.cssText = kameleoonCc;
} else {
kameleoonStn.appendChild(document.createTextNode(kameleoonCc));
}
kameleoonS.parentNode.insertBefore(kameleoonStn, kameleoonS);
window.kameleoonDisplayPage = function(fromEngine) {
if (!fromEngine) {
window.kameleoonTimeout = true;
}
if (kameleoonStn.parentNode) {
kameleoonStn.parentNode.removeChild(kameleoonStn);
}
};
window.kameleoonDisplayPageTimeOut = window.setTimeout(window.kameleoonDisplayPage, kameleoonLoadingTimeout);
}
var scriptNode = document.createElement("script");
scriptNode.src = "//SITE_CODE.kameleoon.io/engine.js";
scriptNode.type = "text/javascript";
scriptNode.async = true;
document.head.appendChild(scriptNode);
While this may technically work, this significantly affect the performance of Kameleoon and introduce a noticeable flicker effect. This is like implementing your own tag manager by doing that: you will suffer all the problems of using a tag manager without any of the associated benefits. Please, really, don't do it.
Is it possible to encrypt data in case of dedicated data-storage clusters (on-premises setup)?
Yes, partitions where data is stored can be encrypted. This option requires an additional setup cost. Contact the Customer Success Manager.
Can I delay non-essential experiments until after the first page load?
Yes, the web experimentation product allows non-essential experiments to be delayed until after the first page load. To delay an experiment, add the DELAYED tag to all experiments to defer. For more information, see the managing tags documentation.
Experiments tagged as "DELAYED" are intelligently managed. Kameleoon doesn't download the configuration until an idle time of at least 10 seconds after the initial page load elapses or until the visitor is being targeted and allocated with a variation that is not the control (reference) variation.
By using this feature, you can focus on delivering the best user experience, as resource-intensive tests won't cause delays or disruptions during the critical page load phase.
How does Kameleoon's platform support scalability and elasticity?
Kameleoon's platform is designed for high scalability and elasticity, ensuring optimal performance as data volumes and user demands grow or during sudden spikes in traffic. The platform currently handles a mean load of 20,000 queries per second, 24/7, 365 days a year, with peaks up to 100,000 queries. For perspective, a typical new customer with 1 million monthly visitors increases this load by only about 100 queries per second. Key factors affecting product scalability include data storage and processing capabilities, system architecture, and load balancing mechanisms:
-
Scalable architecture: Kameleoon uses a distributed and modular architecture, allowing for horizontal scaling. This enables the platform to dynamically add or remove resources based on real-time demand, ensuring continuous performance even during traffic surges.
-
Auto-scaling infrastructure: Leveraging cloud-based infrastructure, Kameleoon can automatically scale up or down its computational resources in response to varying workloads. This ensures that the system can handle peak loads efficiently without manual intervention.
-
Load Balancing: Advanced load balancing techniques are employed to distribute incoming traffic evenly across multiple servers. This prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, ensuring balanced resource utilization and optimal performance.
-
Data ingestion and processing: Kameleoon's data-ingestion tier uses robust APIs and a data broker to classify, buffer, and route incoming data efficiently. This design enhances resilience and performance, allowing the system to manage large volumes of data during traffic spikes.
-
Testing for scalability: Regular load and stress testing are conducted to simulate high-traffic scenarios. These tests help identify potential bottlenecks and ensure that the system can handle extreme conditions without performance degradation.
-
Elastic data storage: The platform uses a combination of in-memory caching, analytics data stores, and raw data repositories to manage data effectively. This multi-tiered storage approach allows for rapid data access and long-term storage scalability.
Which databases and frameworks does Kameleoon use?
The following NoSQL databases and technologies are used in the data flow architecture:
- Hadoop File System (along with Spark)
- Cassandra
- ClickHouse
- Kafka
What network requests does the Kameleoon engine make?
The Kameleoon engine initiates several network requests to ensure seamless functionality. Here are the main requests:
Segments Request:
- Purpose: Collects events for targeted segments by the visitor.
- Endpoint:
https://${SITECODE}.kameleoon.io/audiences/segments.js - Method: GET
- Note: The file is cached for 90 minutes.
Live-update Experiments Configuration Request:
- Purpose: Retrieves LIVE-UPDATE tagged experiments configuration.
- Endpoint:
https://${SITECODE}.kameleoon.io/live-experiments/config.js - Method: GET
- Note: The file is cached for 2 minutes.
Deferred Experiment Variation Request:
- Purpose: Loads variation data for DELAYED tagged experiments.
- Endpoint:
https://${SITECODE}.kameleoon.io/experiments/${action.id}/variations/${variationId}.js - Method: GET
- Note: The file is cached for 30 days.
Deferred Personalization Variation Request:
- Purpose: Loads variation data for DELAYED tagged personalizations.
- Endpoint:
https://${SITECODE}.kameleoon.io/personalizations/${action.id}/variations/${variationId}.js - Method: GET
- Note: The file is cached for 30 days.
Previous Visits Request:
- Purpose: Obtains previous visits for cross-device reconciliation and real-time sync of visits for SDKs.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/visit/visitor
- Method: GET
Tracking Events Request:
- Purpose: For tracking purposes, records events during visits.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/visit/events
- Method: POST
Kameleoon sends an event every 15 seconds when a scroll or click occurs on a page. This ensures the correct session length is tracked for a visitor. If no activity is detected, no additional tracking call is made.
IP address Request:
- Purpose: Exclusively for targeting purposes, enabling the exclusion/inclusion of visitors based on their IP Address.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/ip
- Method: GET
- Note: Kameleoon never stores IPs in databases nor uses them for analytics. The user's IP is employed solely for comparison to an exclusion/inclusion list within the visitor's browsers.
Geolocation Request:
- Purpose: Obtains geolocation data (country, region, or city) for both targeting and analytics purposes.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/geolocation
- Method: GET
Current Weather Request:
- Purpose: Returns the current weather conditions for the user's location. The response includes:
- Temperature data (
temp,feels_like,temp_min,temp_max) - Atmospheric pressure (
pressure,sea_level,grnd_level) - Humidity level
- Weather conditions (
main,description,icon) - Cloud coverage percentage (
clouds["all"]) - Wind information (
speed,deg) - Visibility (in meters)
- Geographic coordinates (
lat,lon) - Location metadata (
name,country,timezone) - Sunrise/sunset timestamps
- Temperature data (
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/weather/weather
- Method: GET
Weather Forecast Request:
- Purpose: Returns a 5-day weather forecast in 3-hour intervals. Each forecast entry includes:
- Temperature (
temp,feels_like,temp_min,temp_max) - Atmospheric pressure (
pressure,sea_level,grnd_level) - Humidity and cloud coverage
- Weather conditions (
main,description,icon) - Wind data (
speed,deg,gust) - Rain volume (if applicable, e.g.
rain["3h"]) - Precipitation probability (
pop) - Visibility
- Timestamp (
dt_txt)
- Temperature (
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/weather/forecast
- Method: GET
Kameleoon Script Detection Request:
- Purpose: Detects the implementation status of the Kameleoon Script on the provided website.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/active-script/event
- Method: POST
Products Request:
- Purpose: Gathers product events for both targeting and product recommendation purposes.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/product/events
- Method: POST
Kameleoon Conversion Scores Request:
- Purpose: Retrieves the latest predictive scores for targeting purposes.
- Endpoint: https://(eu|na)-data.kameleoon.(eu|io)/predict/latestPredictionScoreHistograms
- Method: GET